Azure AI Translator
This application build around the Azure AI Translator API. Azure AI Translator is a cloud-based neural machine translation service that can be used with any operating system. It powers many Microsoft products and services for language translation and other language-related operations. The service uses modern neural machine translation technology and offers statistical machine translation technology.
Before setting up
Before setting up the connection you must be known with the following:
- In order to get
Document translation endpointyou can find documentation here. Note, that Document Translation is supported in the S1 Standard Service Plan (Pay-as-you-go) and C2, C3, C4, and D3 Volume Discount Plans. See Azure AI services pricing—Translator - You can find how to get
API keyhere - If you are unsure about your region you can try
globalas a default value. You can find more information here
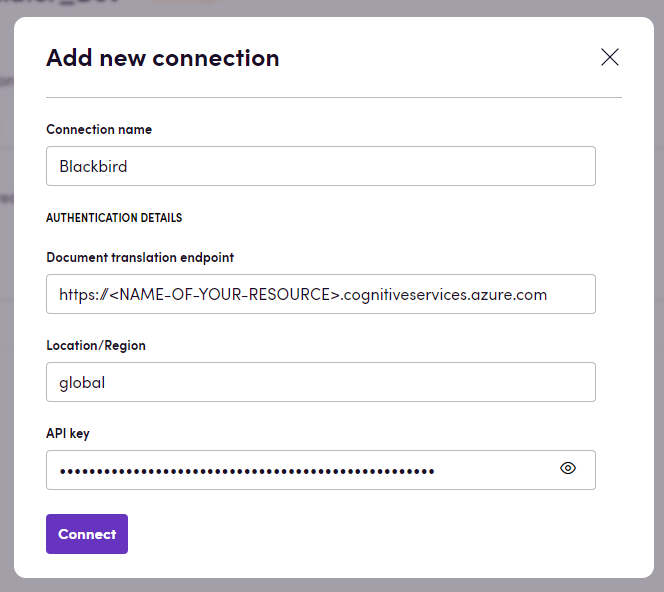
Connecting
- Navigate to Apps, and identify the Azure AI Translator app. You can use search to find it.
- Click Add Connection.
- Name your connection for future reference e.g. ‘My organization’.
- Fill all the required fields:
Document translation endpoint- The endpoint for the document translation service. We expect something like this: https://[NAME-OF-YOUR-RESOURCE].cognitiveservices.azure.com.API key- The API key for the document translation service.Region- The region where the document translation service is hosted.
- Click Connect.
- Confirm that the connection has appeared and the status is Connected.
Actions
Translate
Translates the text to the target language. This action supports the following input parameters:
- Text: The text to be translated.
- Target language: The language to which the text will be translated.
- Source language: The language of the input text. If not specified, automatic language detection is applied.
- Text type: Defines whether the text being translated is plain text or HTML. Possible values are:
plainorhtml. - Category: Specifies the category (domain) of the translation, used to get translations from a customized system.
- Profanity action: Specifies how profanities should be treated in translations. Possible values are:
NoAction,Marked, orDeleted. - Profanity marker: Specifies how profanities should be marked in translations. Possible values are:
AsteriskorTag. - Include alignment: Specifies whether to include alignment projection from source text to translated text. Possible values are:
trueorfalse. - Include sentence length: Specifies whether to include sentence boundaries for the input text and the translated text. Possible values are:
trueorfalse. - Suggested from: A fallback language if the language of the input text can’t be identified.
- From script: The script of the input text.
- To script: The script of the translated text.
- Allow fallback: Specifies that the service is allowed to fall back to a general system when a custom system doesn’t exist. Possible values are:
trueorfalse. Allow fallback = false specifies that the translation should only use systems trained for the category specified by the request. If a translation from language X to language Y requires chaining through a pivot language E, then all the systems in the chain (X → E and E → Y) need to be custom and have the same category. If no system is found with the specific category, the request returns a 400 status code. Allow fallback = true specifies that the service is allowed to fall back to a general system when a custom system doesn’t exist.
As this documentation mentions, if you want to translate text with a custom model, you should specify the category optional input and provide the ID of your custom category in this field.
Example of a category ID: a2eb72f9-43a8-46bd-82fa-4693c8b64c3c-TECH
Translate document
Translates the document to the target language, using synchronous translation under the hood. The action returns the translated document. This action supports the following input parameters:
- File: The document file to be translated.
- Target language: The language to which the document will be translated.
- Source language: The language of the input document. If not specified, automatic language detection is applied.
- Category: Specifies the category (domain) of the translation, used to get translations from a customized system.
- Allow fallback: Specifies that the service is allowed to fall back to a general system when a custom system doesn’t exist. Possible values are:
trueorfalse. Allow fallback = false specifies that the translation should only use systems trained for the category specified by the request. If a translation from language X to language Y requires chaining through a pivot language E, then all the systems in the chain (X → E and E → Y) need to be custom and have the same category. If no system is found with the specific category, the request returns a 400 status code. Allow fallback = true specifies that the service is allowed to fall back to a general system when a custom system doesn’t exist.
Supported file formats can be found here.
Transliterate
Transliterates the text to the target script. This action supports the following input parameters:
- Text: The text to be transliterated.
- Source language: The language of the input text.
- Source script: Specifies the script used by the input text.
- Target script: Specifies the script to which the text will be transliterated.
Example
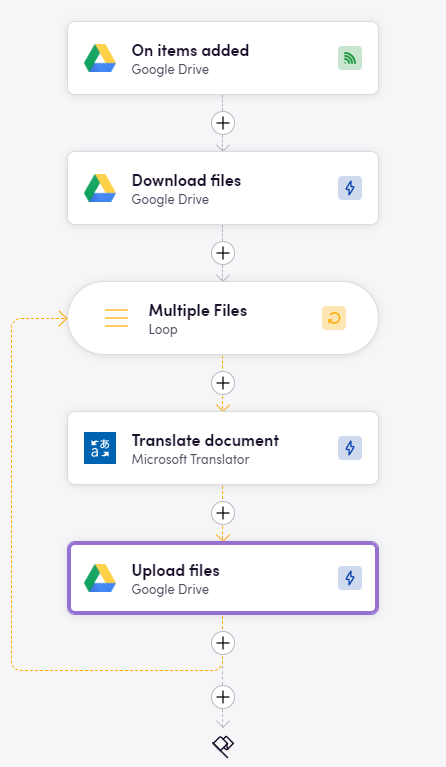
Here is an example of how you can use the Azure AI Translator app in a workflow. In this example, we are translating a document from Google Drive to the target language and then sending the translated document back to a different folder.
Feedback
Do you want to use this app or do you have feedback on our implementation? Reach out to us using the established channels or create an issue.